- Categories
- Contact
-
Mobile: +86 19533187458
WeChat: +86 19533187458
WhatsApp: +86 19533187458
- drive shaft drive shaft
- drive shaft
drive shaft
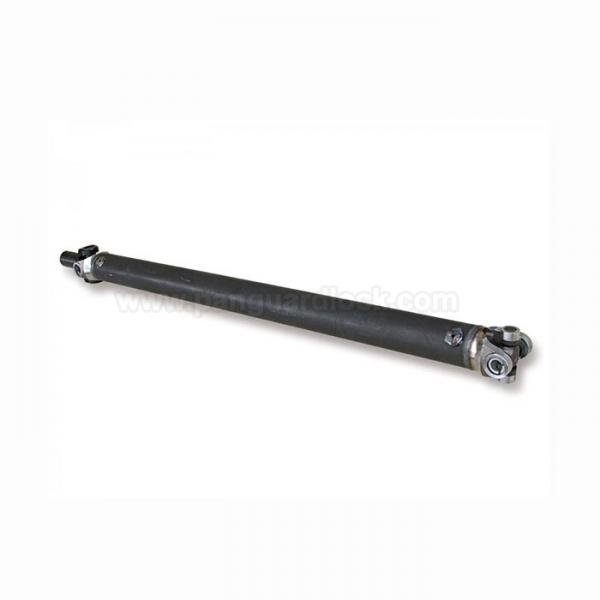
A drive shaft is a mechanical component used to transmit torque (rotational power) from an engine or motor to the wheels or other driven parts of a machine. It is a crucial part of a vehicles drivetrain system, often referred to by other names such as a propeller shaft (prop shaft) or Cardan shaft.
Enquiry Now
The main purpose of a drive shaft is to connect components that cannot be linked directly because of distance or the need for relative movement between them, such as when a vehicles suspension moves up and down.
Drive shafts are typically made of strong, lightweight materials like steel or aluminum and incorporate specific components to allow for flexibility and smooth power transmission:
• Tube/Shaft: The main body of the drive shaft, designed to withstand high levels of torque and rotational forces.
• Universal Joints (U-joints): Located at the ends of the shaft, these flexible joints (often cross-shaped) allow the drive shaft to operate at various angles, accommodating the movement of the vehicles suspension and steering.
• Slip Yoke/Spline: A component that allows the drive shaft to lengthen or shorten as the distance between the transmission/transfer case and the differential changes.
• Flange/Yoke: The end fittings that provide a secure connection point to the transmission, transfer case, or differential.
• Center Support Bearing: Used in longer, two-piece drive shafts to provide additional support and minimize vibrations.
Types and Applications
The specific design of a drive shaft varies depending on the type of vehicle:
• Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) & Four-Wheel Drive (4WD): These vehicles use a long drive shaft to transmit power from the front-mounted engine/transmission (or transfer case in 4WD) to the rear differential.
• Front-Wheel Drive (FWD): FWD vehicles typically use shorter, more complex constant velocity (CV) shafts (or half shafts) which incorporate CV joints to deliver power to the front wheels while allowing for a wide range of steering angles.
• Other Applications: Drive shafts are also used in various other systems, including industrial machinery, marine vessels (propeller shaft), and some motorcycles and aircraft.
Common Symptoms of Failure
A failing drive shaft can cause a range of issues. Key signs include:
• Intense vibration coming from underneath the vehicle.
• Clunking sounds when shifting gears, accelerating, or turning.
• Squeaking or grinding noises during driving.
• Problems with turning or unresponsive steering.
If any of these symptoms occur, it is essential to have the drive shaft inspected by a professional, as a complete failure can cause significant damage or lead to a loss of control of the vehicle.
- You may also like (Related items of drive shaft)
- drive shaft(Shafts) has been presented above, want more related products, please click the category below.
Category: Custom Drive Shafts
Related category: - Bookmark this pagePrint this page