- Categories
- Contact
-
Mobile: +86 19533187458
WeChat: +86 19533187458
WhatsApp: +86 19533187458
- Universal joints Universal joint
- Universal joint
Universal joints
Drive shafts, also known as propeller shafts or cardan shafts, are cylindrical mechanical components used to transmit torque and rotational motion from an engine or transmission to the drive wheels or other components that cannot be directly connected due to distance or angle changes. They are essential in various vehicle and industrial applications to deliver power efficiently and accommodate movement.
Enquiry Now
Design and Function
The main challenge drive shafts overcome is transmitting power between components that are not on the same axis or whose relative positions change during operation, such as with vehicle suspension movement.
Power Transmission: They act as a critical link in the powertrain, transferring engine power to the differentials, which then turn the wheels.
Accommodating Movement: They incorporate joints, such as universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints, which allow the shaft to flex and operate at different angles without breaking the drivetrain components.
Vibration Absorption: Drive shafts are designed and balanced to absorb vibrations generated during operation, contributing to a smoother, quieter, and more stable ride.
Length Compensation: Many drive shafts, especially in vehicles, feature a telescopic design or a slip joint that allows the shaft to change length slightly to accommodate the vertical movement of the suspension.
Materials
Drive shafts must be strong enough to withstand high torque and stress while being light enough to ensure efficiency. Materials are selected based on the specific application's requirements.
Steel: The most common material due to its high strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Various carbon and alloy steels are used for different strength requirements.
Aluminum Alloys: Offer a significant weight advantage over steel, which can improve fuel efficiency and performance in racing or light vehicles. They also have good corrosion resistance.
Composite Materials (e.g., Carbon Fiber): Used in high-performance and aerospace applications due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, high damping capacity (vibration absorption), and corrosion resistance.
Types of Drive Shafts
The type of drive shaft used depends heavily on the vehicle's drivetrain configuration.
One-Piece Drive Shaft: A single, long shaft commonly used in passenger cars and light trucks with a shorter wheelbase. It offers simplicity and reduced vibration over short distances.
Two-Piece Drive Shaft: Used in longer vehicles like full-sized trucks and SUVs. It consists of two shorter shafts connected by a center support bearing to reduce vibration over the increased distance.
Constant Velocity (CV) Axle Shafts: Predominantly found in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, these shafts use CV joints to transmit power to the wheels at a constant rotational speed, even at sharp steering angles or during suspension movement.
Propeller (Prop) Shaft: A term often used interchangeably with drive shaft, specifically referring to the long, longitudinal shaft in rear-wheel-drive vehicles that connects the transmission to the rear differential. - You may also like (Related items of Universal joints)
- Universal joints has been presented above, want more related products, please click the category below.
Category: Universal joints
Related category: - Bookmark this pagePrint this page
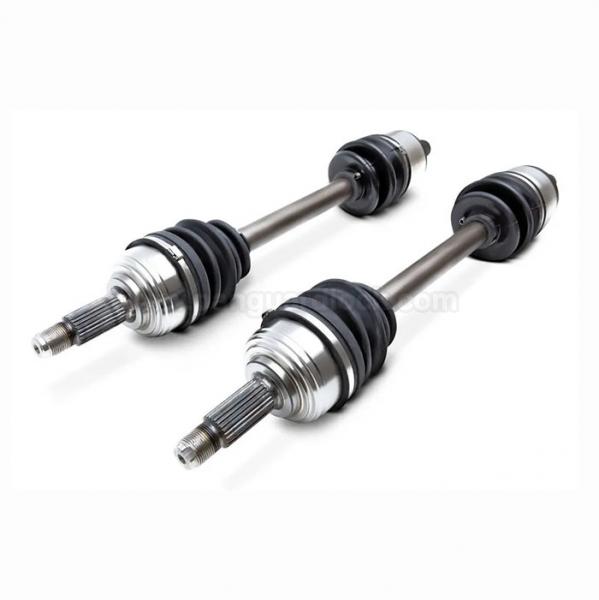



 Universal joints
Universal joints