- Categories
- Contact
-
Mobile: +86 19533187458
WeChat: +86 19533187458
WhatsApp: +86 19533187458
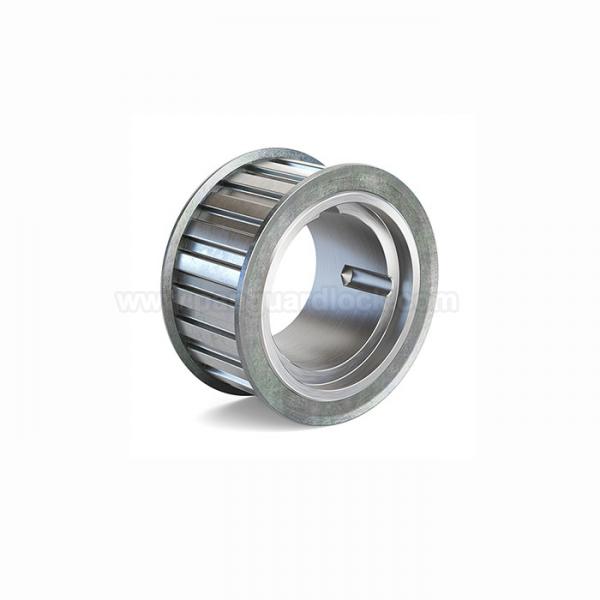
- Timing pulleys Timing pulleys
- Timing pulleys
Timing pulleys
Timing pulleys are essential mechanical components with teeth or pockets around their outer diameter that mesh with corresponding teeth on a timing belt to transmit power and rotational motion without slippage. This positive engagement ensures precise synchronization between shafts, which is critical in applications requiring accurate indexing or sequencing.
Enquiry Now
Design and Function
Timing pulleys operate like a chain and sprocket system but with a belt, offering a reliable, low-maintenance, and quiet power transmission method.
Positive Drive: Power transmission occurs through the mechanical interlocking of teeth, not friction. This eliminates the risk of slippage, maintaining a constant speed ratio and precise positioning.
Synchronization: The primary use is to link two or more shafts in synchronous rotation. This is vital for operations like ensuring engine valves open and close in perfect sequence with the pistons.
Low Maintenance: Because the power is transmitted via meshing teeth and not surface contact, timing belt systems require no lubrication and less initial tension, which reduces maintenance needs and bearing loads on the shafts.
Efficiency: Timing pulley drives are highly efficient (around 99%) and provide positive acceleration and braking.
Types and Materials
Timing pulleys are defined by their tooth geometry (pitch) and material, which are selected based on the specific application's requirements.
Tooth Profiles
Trapezoidal Profile (MXL, XL, L, H): An older, inch-based profile offering very good positioning accuracy at low cost, suitable for general-purpose applications.
Curvilinear Profile (HTD 3mm, 5mm, 8mm; GT2, GT3): Features a rounded, deeper tooth profile for a more even load distribution, higher torque capacity, and reduced risk of the belt jumping teeth.
Materials
Aluminum: A common choice for its balance of durability, lightweight, and corrosion resistance, often used in high-speed or high-precision equipment like robotics and CNC machines.
Steel (e.g., 45# Steel): Offers superior strength and durability for heavy-duty, high-load applications, though it is heavier than aluminum and typically requires surface treatment (like blackening or galvanizing) for corrosion resistance.
Plastic (e.g., Nylon, Acetal): The lightest and most affordable option, suitable for low-load applications or environments where corrosion resistance and low noise are priorities. Some plastics have self-lubricating properties which can help prevent belt wear.
Common Applications
Timing pulleys are used where precision and synchronization are critical.
Automotive Engines: Synchronizing the rotation of the camshaft and crankshaft to ensure proper engine timing.
Robotics: Coordinating the movement of robotic arms for high accuracy in complex tasks.
CNC Machines and 3D Printers: Providing precise and repeatable motion control for accurate manufacturing.
Conveyor Systems: Ensuring that items are moved at the correct, consistent speed and sequence.
Office Equipment: Found in printers, scanners, and other office machinery where precise paper handling is necessary. - You may also like (Related items of Timing pulleys)
- Timing pulleys has been presented above, want more related products, please click the category below.
Category: Timing pulleys
Related category: - Bookmark this pagePrint this page