- Categories
- Contact
-
Mobile: +86 19533187458
WeChat: +86 19533187458
WhatsApp: +86 19533187458
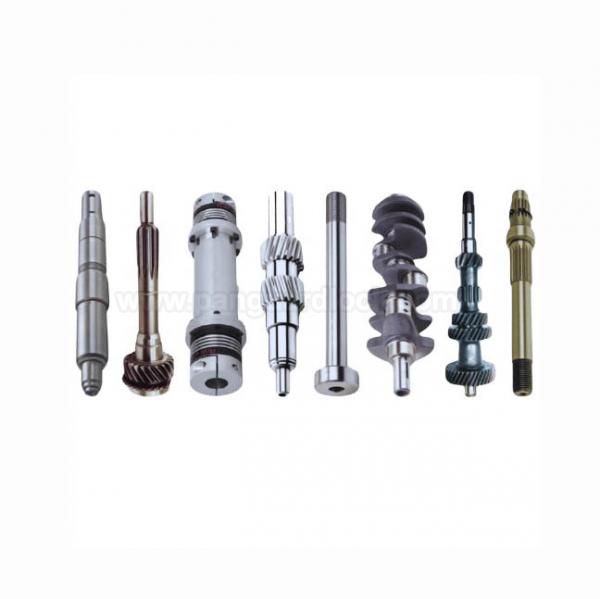
- Shafts for Special Equipment Shafts for Special Equipment
- Shafts for Special Equipment
Shafts for Special Equipment
Shafts for special equipment are custom-engineered components designed to meet the specific demands of specialized machinery across various industries, often requiring particular materials and precision manufacturing to transmit power and withstand severe conditions.
Enquiry Now
Types of Shafts for Special Equipment
• Cardan Shafts/Universal Joint Shafts: Used when power needs to be transmitted between non-aligned components or where angles and directions of movement change, such as in agricultural equipment (tractors, combine harvesters) and heavy industrial machinery.
• PTO (Power Take-Off) Drive Shafts: Specialized for agricultural and construction equipment to transfer power from the power source (e.g., tractor) to the implement, available in various telescoping profiles like lemon, star, square, or spline to ensure a secure fit and efficient power transfer.
• Crankshafts: Integral parts of engines in various applications (automotive, marine, energy) that convert linear piston motion into rotational motion and are designed to handle harsh loading conditions and fatigue.
• Pump Shafts: Designed for use in pumps, compressors, and other fluid-handling machinery, often requiring materials resistant to corrosion, vibration, and bending loads.
• Precision/Spindle Shafts: Used in applications requiring high accuracy and tight tolerances, such as robotic surgical equipment, aircraft instruments, machine tools (lathes, milling machines), and automation systems.
• Hollow Shafts: Used when weight reduction is critical (e.g., aerospace and racing vehicles), as they offer less weight for nearly the same stiffness as solid shafts of the same diameter.
Common Materials and Properties
The selection of materials is critical and depends heavily on the specific application”s load, environment, and performance requirements.
• Alloy Steels (e.g., AISI 4140, 4340): Offer high strength and toughness, suitable for heavy-duty, high-stress applications like drive shafts and crankshafts.
• Stainless Steel (e.g., 17-4PH, AISI 304): Provides excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for marine environments, food processing, and chemical industries.
• Carbon Steel (e.g., Mild Steel, Ck45): Commonly used for general-purpose shafts due to its affordability and good machinability.
• Aluminum: Selected when weight reduction is essential due to its lightweight nature and corrosion resistance.
• Specialty Materials (e.g., PEEK, Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer, Titanium): Used for applications requiring specific properties such as high corrosion resistance, self-lubrication, high temperature resistance, or an optimal strength-to-weight ratio.
Specialized Manufacturing and Sourcing
Given the need for specialized equipment, these shafts are often custom manufactured to exact specifications and tight tolerances.
• Custom Manufacturers: Companies such as AmTech International, Western Machine Works, and Ondrives.US specialize in producing custom-engineered shafts using advanced techniques like forging, precision machining, and casting to meet specific OEM standards.
• Stock & Aftermarket Suppliers: For common applications in industries like agriculture and construction, new and used shafts and components are available from large industrial suppliers and online marketplaces such as eBay and Machineryline USA, which carry parts compatible with brands like John Deere, Case IH, and Caterpillar.
- You may also like (Related items of Shafts for Special Equipment)
- Shafts for Special Equipment(Shafts) has been presented above, want more related products, please click the category below.
Category: Custom Profile Gears
Related category: - Bookmark this pagePrint this page



 Custom Profile Gears
Custom Profile Gears