- Categories
- Contact
-
Mobile: +86 19533187458
WeChat: +86 19533187458
WhatsApp: +86 19533187458
- Self-lubricating plastic bearings Self-lubricating plastic bearings
- Self-lubricating plastic bearings
Self-lubricating plastic bearings
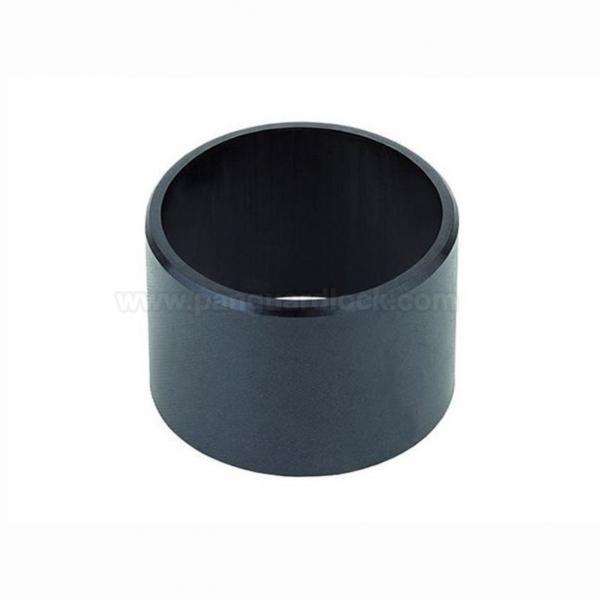
Self-lubricating plastic bearings are sliding bearings made from engineered polymers or composite materials that contain integrated solid lubricants. They operate without external oil or grease lubrication, making them ideal for applications requiring clean operation, corrosion resistance, and maintenance-free performance.
Enquiry Now
Key Features and Benefits
Maintenance-Free: The embedded lubricants provide continuous lubrication for the entire service life, eliminating the need for periodic re-greasing and reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance: Most engineering plastics (like POM, Nylon, and PTFE) are inherently resistant to a wide range of chemicals, water, and UV radiation, making them ideal for harsh environments where metal bearings would fail.
Clean Operation: Without external oils or greases, there is no risk of lubricant leakage, which is crucial for hygiene-sensitive applications (food processing, medical) or environments where cleanliness is paramount.
Lightweight and Quiet: Plastics are significantly lighter than metals. They also offer excellent vibration damping, contributing to quieter operation and reduced noise pollution.
Contamination Tolerance: The softer polymer surface allows small dirt or dust particles to be embedded harmlessly, preventing damage to the mating shaft.
Non-Magnetic/Electrical Insulation: As non-conductive materials, they are suitable for use in electronic equipment or magnetic environments (like MRI machines).
Types of Self-Lubricating Plastic Bearings
The type of plastic and construction method varies depending on the specific application requirements:
Solid Polymer Bearings:
Description: Machined or molded from a single block of plastic, often containing internal lubricants (e.g., oil-filled nylon, PTFE-filled acetal).
Use Cases: General industrial use, food processing, and marine applications requiring chemical resistance and dimensional stability.
Metal-Polymer Composite Bearings (Lined):
Description: These are multi-layer bearings with a metal backing (steel or bronze) for strength, a porous sinter metal interlayer, and a thin, self-lubricating polymer sliding layer (e.g., PTFE or Acetal).
Use Cases: Excellent for high loads, oscillating movements, and dirty environments, common in automotive suspension systems and hydraulic pumps.
Filament Wound Composite Bearings:
Description: High-strength fibers (fiberglass) are wound and resin-impregnated with a self-lubricating inner liner.
Use Cases: Demanding applications requiring extremely high static loads, such as aerospace flight control systems and heavy-duty industrial pivots.
Applications
Self-lubricating plastic bearings are widely used across diverse industries due to their performance advantages:
Food and Beverage Processing: Conveyor systems and packaging equipment requiring frequent washdowns and hygiene compliance.
Automotive Industry: Steering systems, window regulators, power seats, and various chassis components.
Medical Equipment: Surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment (MRI scanners), and patient handling systems due to their cleanliness and non-magnetic properties.
Marine and Subsea: Pumps, valves, and control systems where resistance to saltwater and operation without external lubrication are essential.
Industrial Automation: Robotics, linear guides, and material handling systems for quiet, reliable operation. - You may also like (Related items of Self-lubricating plastic bearings)
- Self-lubricating plastic bearings has been presented above, want more related products, please click the category below.
Category: Self-Lubricating Plastic Bearings
Related category: - Bookmark this pagePrint this page