- Categories
- Contact
-
Mobile: +86 19533187458
WeChat: +86 19533187458
WhatsApp: +86 19533187458
- Planetary Gears Planetary Gears
- Planetary Gears
Planetary Gears
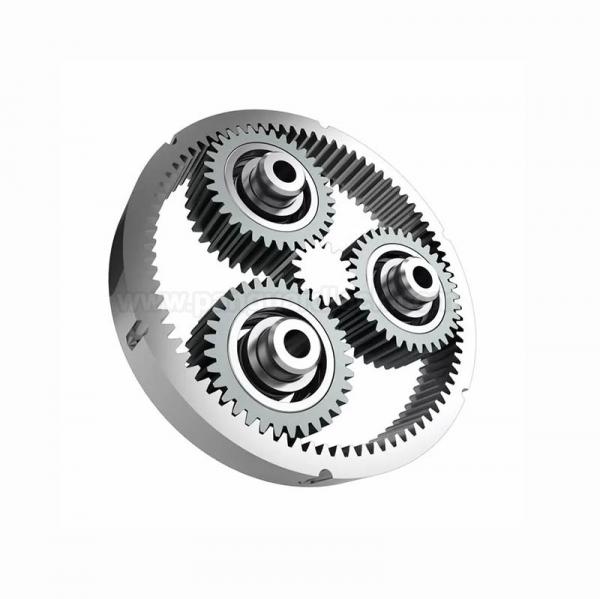
A planetary gear system, also known as an epicyclic gear train, is a gear arrangement in which one or more outer "planet" gears revolve around a central "sun" gear while also rotating on their own axes. This design is highly valued in engineering for its compactness, high efficiency, and ability to transmit high torque loads.
Enquiry Now
Components of a Planetary Gear System
A basic planetary gear set consists of four main components:
• Sun gear: The central gear (like the Sun in our solar system) that receives the input power or drives the system.
• Planet gears: Multiple smaller gears that mesh with the sun gear and orbit around it (like planets).
• Ring gear: An outer ring with inward-facing teeth that meshes with the planet gears and encircles the entire assembly.
• Planet carrier: A movable frame or arm that connects and holds the planet gears in their positions and typically serves as the output or input component.
How It Works
The operational principle of a planetary gear system is highly versatile because different gear ratios and rotational directions can be achieved by holding one of the main components stationary and using the other two as input and output.
• Speed Reduction (Most Common): Typically, the ring gear is held stationary, the sun gear is the input (high speed, low torque), and the planet carrier is the output (lower speed, higher torque).
• Other Configurations: By fixing the sun gear or the carrier, the system can achieve different functions, including reversing the direction of rotation or increasing speed.
Advantages
Planetary gears offer several benefits compared to traditional parallel-axis gear systems:
• Compact design: The coaxial alignment of the input and output shafts allows for high gear reduction ratios in a small space.
• High torque capacity: The load is distributed among multiple planet gears, allowing the system to handle significantly higher torque loads with less wear.
• Efficiency: The load sharing design results in high power transmission efficiency, often around 97% per stage.
• Durability: Even load distribution makes the gears more resistant to damage and provides a longer service life.
Common Applications
Planetary gear systems are used in a wide range of applications that demand high torque density and efficiency:
• Automotive transmissions: They form the basis of most modern automatic transmissions, enabling smooth and efficient gear shifting.
• Robotics: Used in robotic arms and manipulators to provide precise motion control and high torque.
• Heavy machinery: Found in tractors, construction equipment, and industrial mixers for wheel and track drives.
• Aerospace & Defense: Utilized in aircraft landing gear systems and satellite positioning mechanisms.
• Wind turbines: Employed to increase the rotational speed from the blades to the generator. - You may also like (Related items of Planetary Gears)
- Planetary Gears(Gears) has been presented above, want more related products, please click the category below.
Category: Planetary Gears
Related category: - Bookmark this pagePrint this page