- Categories
- Contact
-
Mobile: +86 19533187458
WeChat: +86 19533187458
WhatsApp: +86 19533187458
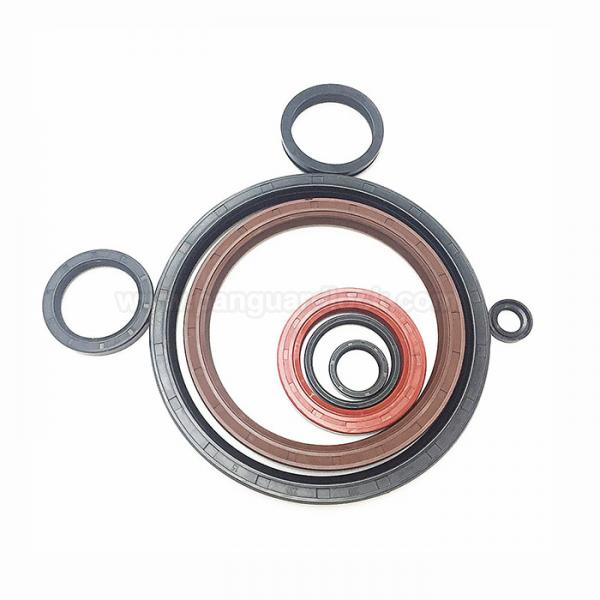
- Non-skeleton oil seals Non-skeleton oil seals
- Non-skeleton oil seals
Non-skeleton oil seals
Non-skeleton oil seals are a category of radial shaft seals that do not contain an internal metal reinforcement case or "skeleton". Instead, the seal's structural integrity and strength are derived solely from a combination of the elastomer material itself (which covers the entire seal) and its design features.
Enquiry Now
Key Features and Benefits
Corrosion Resistance: Because the seal is entirely covered by rubber (or a similar elastomer), the internal components, if any, are protected from corrosive fluids and environments. This makes them ideal for marine, food processing, and chemical applications.
Good Static Sealing: The fully rubberized outer diameter provides an excellent static seal in the housing bore, even if the bore is slightly rough or subject to minor thermal expansion differentials.
Accommodates Imperfections: The flexible nature of the all-rubber exterior allows the seal to conform better to minor imperfections in the housing bore.
Ease of Installation: The absence of sharp metal edges simplifies installation and reduces the risk of damage to the housing bore during fitting.
Lubricant Retention and Contamination Protection: Like other oil seals, they feature a primary sealing lip (often spring-loaded) to contain lubricants and a secondary lip (in double lip versions) to exclude contaminants.
Common Materials
The elastomer material used is crucial as it provides both the sealing function and the structural integrity:
Nitrile (NBR / Buna-N): A common and cost-effective material offering good resistance to petroleum-based oils and greases.
Viton® (FKM): Used for applications requiring resistance to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals.
Silicone (VMQ): Offers superior flexibility and performance in extreme low and high temperatures.
EPDM: Primarily used for resistance to water, steam, and ozone in non-oil-based applications.
Applications
Non-skeleton oil seals are suitable for applications where corrosion resistance, a superior static seal in the bore, and reliable lubricant retention/contamination exclusion are necessary:
Food and Beverage Processing: In machinery where seals must resist cleaning agents and prevent corrosion, often using FDA-approved materials.
Marine Applications: In boat and offshore equipment where saltwater corrosion is a concern.
Industrial Machinery: Found in pumps and gearboxes where the housing bore may have minor surface imperfections or where chemical resistance is required.
General Engineering: Employed in various mechanical systems where the benefits of an all-rubber exterior are preferred. - You may also like (Related items of Non-skeleton oil seals)
- Non-skeleton oil seals has been presented above, want more related products, please click the category below.
Category: Non-Skeleton Oil Seals
Related category: - Bookmark this pagePrint this page