- Categories
- Contact
-
Mobile: +86 19533187458
WeChat: +86 19533187458
WhatsApp: +86 19533187458
- Linear guides Linear guides
- Linear guides
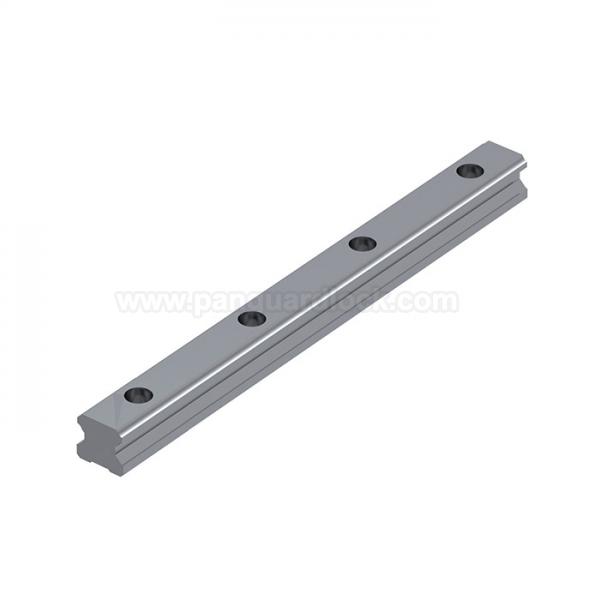
Linear guides
Linear guides, also known as linear guideways or slide rails, are mechanical systems designed to provide precise, low-friction straight-line movement while supporting significant loads. They are composed of a stationary rail (track) and a moving carriage (block) that facilitate controlled, repeatable motion in machinery across many industries.
Enquiry Now
MGN12-200mm Linear Guide Rail Set | Sienci Labs
Linear guides | cpc Europe - Excellence in motion
Key Features and Benefits
High Precision and Accuracy: Linear guides are manufactured to very tight tolerances, ensuring minimal deviation from the intended path and high repeatability, which is crucial for precision applications.
Low Friction: By utilizing rolling elements (balls or rollers) or self-lubricating sliding surfaces, friction is significantly reduced (the coefficient can be 1/50th of traditional sliding guides), leading to smoother motion, lower energy consumption, and less wear.
High Load Capacity and Rigidity: They are robustly designed with optimized raceway geometries (like the gothic arch or O-arrangement) to handle heavy static, dynamic, and moment loads while maintaining high stiffness to prevent deflection and vibration.
Versatility and Adaptability: Available in numerous sizes and materials (steel, stainless steel, aluminum, plastic composites), linear guides can be tailored to specific application requirements and environments.
Long Travel Distance: Many designs, particularly those with recirculating rolling elements, allow for virtually unlimited stroke lengths, limited only by the length of the guide rail.
Common Types
Linear guide systems are generally categorized by their underlying motion mechanism and rail profile:
Recirculating Ball Guides: The most common type, using continuously circulating steel balls for low friction, high speed, and versatility in applications from 3D printers to high-speed machining centers.
Roller Guides: Utilize cylindrical or tapered rollers to support heavier loads and provide greater rigidity and shock resistance than ball guides. They are often used in heavy industrial machinery.
Plain (Sliding) Guides: Rely on sliding contact between two surfaces, often using self-lubricating materials like PTFE or Acetal. They are tolerant of dirt and vibration but have higher friction and are better suited for lower speeds and less precise applications like woodworking equipment or high-contamination environments.
Profiled Rail Guides (Square Rails): Feature precision-ground, square-edged rails and bearing blocks that provide high rigidity and load capacity in all directions. They are the standard for high-performance CNC machines and industrial automation.
Round Rail Guides: A cost-effective option using cylindrical shafts and ball bushings. They are simple to install and accommodate shaft misalignments well, often used in general automation and 3D printers.
Applications
Linear guides are indispensable in a wide range of industries for precision motion control:
CNC Machines and Machine Tools: Provide the high precision and rigidity required for accurate cutting, milling, and drilling operations.
Robotics and Automation Systems: Enable the smooth, repeatable movements of robotic arms, pick-and-place machines, and automated assembly lines.
Medical and Laboratory Equipment: Used in scanners, surgical robots, and diagnostic equipment where smooth, precise motion is paramount.
Semiconductor Manufacturing: Essential for handling wafers and other components in a cleanroom environment with extremely high precision.
3D Printing: Ensure accurate layer deposition and smooth movement of the print head and build platform. - You may also like (Related items of Linear guides)
- Linear guides has been presented above, want more related products, please click the category below.
Category: Linear guides
Related category: - Bookmark this pagePrint this page