- Categories
- Contact
-
Mobile: +86 19533187458
WeChat: +86 19533187458
WhatsApp: +86 19533187458
- Flat springs Flat springs
- Flat springs
Flat springs
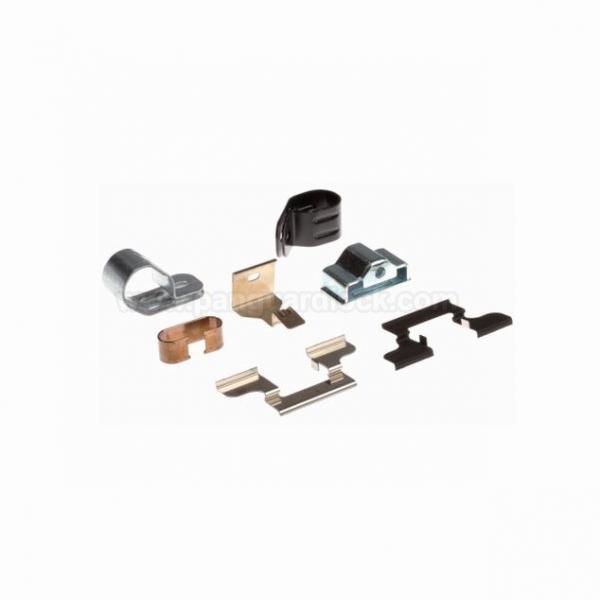
Flat springs are mechanical components made from flat strips of metal that store and release energy through elastic bending stress, not the torsional stress found in coiled springs. They are highly versatile, offered in numerous shapes, and are ideal for applications in compact spaces.
Enquiry Now
Design and Function
Flat springs function by deflecting (flexing or bending) when an external load is applied and return to their original shape when the load is removed, releasing the stored energy.
Space Efficiency: Their low-profile, flat design makes them a top choice for use in constrained or small areas where coiled springs may not fit.
Versatility: They can be custom-formed into unique configurations to serve specific functions beyond just springing, such as clips, clamps, or electrical contacts.
Force Characteristics: They can be designed to provide a specific force or serve as part of a mounting assembly, with force determined by material, thickness, and design.
Types of Flat Springs
The category of "flat springs" encompasses several distinct designs:
Cantilever Springs: Fixed at one end and free at the other (like a diving board), used in switches, relays, and precision instruments where controlled deflection is needed.
Belleville Washers (Disc Springs): Conical-shaped discs that offer high force in minimal axial space, commonly used for bolt preloading in heavy-duty applications.
Leaf Springs: Consisting of single or multiple layers of metal strips, these are a traditional component in vehicle suspension systems for supporting heavy loads and absorbing shock.
Wave Springs: Made from flat wire coiled into a wavy pattern, providing the same force as a coil spring but with a much lower operating height, ideal for bearing preloading.
Constant Force Springs: Flat wound strips that provide a nearly constant force over a very long range of linear motion, found in tape measures and counterbalancing systems.
Materials
Material selection is critical and based on the required strength, corrosion resistance, and operating environment.
Carbon Steel (e.g., Music Wire, SAE 1070-1090): Offers high strength and durability, typically requiring protective coatings in corrosive environments.
Stainless Steel (e.g., Type 301, 316, 17-7PH): Provides excellent corrosion and heat resistance, suitable for medical, marine, and food processing applications.
Copper and Nickel Alloys (e.g., Beryllium Copper, Phosphor Bronze): Used in applications requiring electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Common Applications
Due to their versatility and space efficiency, flat springs are used across numerous industries.
Electronics: Providing reliable electrical contacts in switches, connectors, and battery compartments.
Automotive Industry: Used in seat mechanisms, pedal assemblies, door handles, and window mechanisms.
Industrial Equipment: Employed in motors, generators, presses, and clamping devices.
Aerospace & Medical: Used in critical control systems and surgical instruments where lightweight and reliable components are essential. - You may also like (Related items of Flat springs)
- Flat springs has been presented above, want more related products, please click the category below.
Category: Flat springs
Related category: - Bookmark this pagePrint this page