- Categories
- Contact
-
Mobile: +86 19533187458
WeChat: +86 19533187458
WhatsApp: +86 19533187458
- Crank Shafts Crank Shafts
- Crank Shafts
Crank Shafts
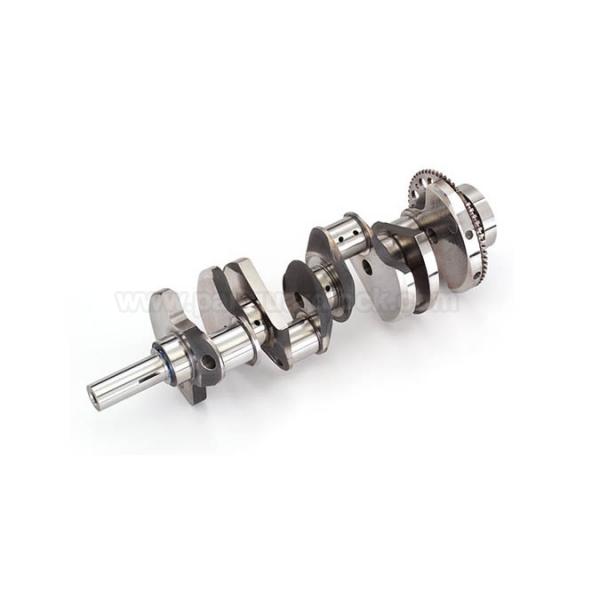
A crankshaft is a vital mechanical component in a piston engine that converts the up-and-down (reciprocating) motion of the pistons into rotational (circular) motion. This rotational energy is then used to power the vehicle wheels or other machinery.
Enquiry Now
Function and Importance
The crankshaft is often referred to as the "heart" of the engine. Its main functions include:
• Energy Conversion: It translates the linear force generated by the combustion of fuel in the cylinders into a usable rotational torque.
• Power Transmission: The resulting torque is transferred through the flywheel and transmission system to the drive wheels.
• Engine Balance: The crankshaft is fitted with counterweights (crank webs) that help balance the forces from the moving pistons, reducing vibration and ensuring smooth engine operation.
• Synchronization: It drives other engine components, such as the camshaft via a timing belt or chain, which is crucial for synchronizing the opening and closing of engine valves.
Key Components
A crankshaft is a complex and heavy-duty component, usually made of forged steel or cast iron, designed to withstand immense stress. Its primary parts include:
• Main Journals: These are the smooth, round sections that the crankshaft rotates on within the engine block, supported by main bearings.
• Crankpins (Rod Journals): These are offset from the main axis of rotation and are where the large end of the connecting rods attach, providing the leverage needed for rotation.
• Crank Webs: These connect the main journals to the crankpins, forming the "arms" of the crank mechanism.
• Counterweights: Masses attached to the crank webs to ensure the assembly is balanced and runs smoothly.
• Oil Passages: Internal channels drilled into the shaft to allow lubricating oil to flow to the various bearings, minimizing friction and wear.
• Flywheel Mounting Flange: A connection point at one end for the flywheel, which stores kinetic energy to smooth out power delivery and maintain momentum.
Applications
While most commonly associated with automotive internal combustion engines, crankshafts are used in various machines that require the conversion of linear to rotary motion (or vice versa), including:
• Motorcycles
• Marine, stationary, and locomotive diesel engines
• Industrial compressors and pumps
• Power generators
- You may also like (Related items of Crank Shafts)
- Crank Shafts(Shafts) has been presented above, want more related products, please click the category below.
Category: Crank Shafts
Related category: - Bookmark this pagePrint this page