- Categories
- Contact
-
Mobile: +86 19533187458
WeChat: +86 19533187458
WhatsApp: +86 19533187458
- Bimetallic bearings Bimetallic bearings
- Bimetallic bearings
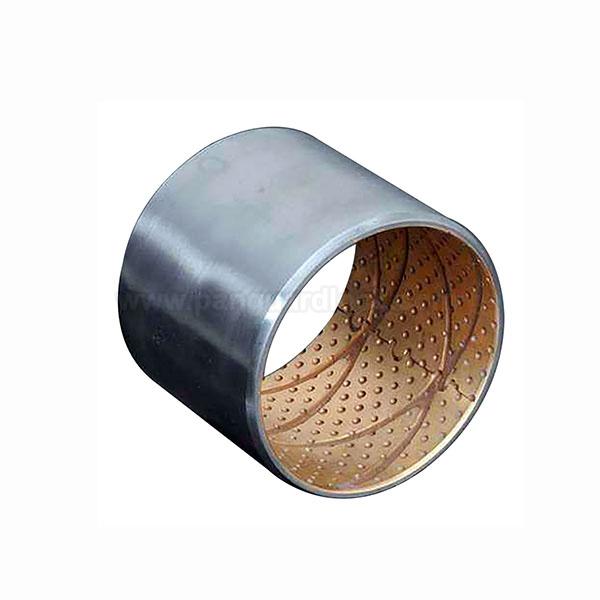
Bimetallic bearings
Bimetallic bearings are composite plain bearings that combine two distinct metal layers to offer high load capacity and durability in a compact, cost-effective design. They typically feature a strong steel backing and a softer, low-friction inner layer of a bronze or aluminum alloy.
Enquiry Now
Key Features and Benefits
High Load Capacity: The robust steel backing provides exceptional structural strength, allowing the bearing to withstand high static, dynamic, and shock loads.
Good Wear Resistance: The softer inner lining material (e.g., bronze or aluminum alloy) offers superior wear resistance and low-friction properties, extending the lifespan of machinery.
Versatility in Lubrication: The friction surface can be designed with specialized oil grooves, pockets, or holes to ensure optimal lubrication distribution, making them adaptable to various conditions and suitable for extended relubrication intervals.
Vibration and Shock Absorption: The dual-layer design helps dampen vibrations and absorb shock loads, contributing to quieter and smoother operation compared to some rolling bearings.
Cost-Effective and Compact: Utilizing a steel base is cost-effective, and the thin-walled, compact design saves space and weight in machinery.
Corrosion Resistance: Specific alloy choices and optional coatings (like copper or tin plating on the steel back) enhance the bearing's corrosion resistance in industrial or humid environments.
Types and Materials
The performance of bimetallic bearings is primarily determined by the composition of their two layers:
Steel Backing: Usually made of low-carbon steel, this layer provides the necessary mechanical strength, rigidity, and dimensional stability.
Sliding Layer (Liner): Sintered or rolled onto the steel, this softer layer provides the actual bearing surface. Common materials include:
Leaded Bronze Alloys: Such as CuPb10Sn10 or CuPb24Sn4, these offer excellent embeddability (ability to trap debris), good lubrication performance, and corrosion resistance.
Lead-Free Bronze Alloys: Environmentally conscious options like CuSn6.5-0.1 are used to meet modern environmental directives while still offering high load capacity and wear resistance.
Aluminum Alloys: Such as AlSn20Cu, these are often used in automotive engines for their moderate fatigue strength, good corrosion resistance, and suitability with unhardened steel shafts.
Applications
Bimetallic bearings are used in a wide range of demanding applications due to their durability and load-bearing capabilities:
Automotive Engines: Widely used as main bearings, connecting rod bushings, and camshaft bushings due to their ability to handle high-frequency oscillations and varying loads.
Heavy Machinery: Essential for construction and mining equipment, such as in excavators, bulldozers (e.g., slave wheel bushings), and hydraulic cylinders.
Industrial Equipment: Found in gear pumps, lifting equipment, compressors, and various industrial machines requiring durable, high-load plain bearings.
Agricultural Machinery: Used in components like kingpin bushings and spherical joint bearings, where rough conditions and heavy loads are common. - You may also like (Related items of Bimetallic bearings)
- Bimetallic bearings has been presented above, want more related products, please click the category below.
Category: Bimetallic Bearings
Related category: - Bookmark this pagePrint this page